North America
Imagine if Jeb Bush or Hillary Clinton had become president in 2016, then won re-election in 2020. There would have been a Bush or a Clinton as president for 28 out of 36 consecutive years, from George H W Bush’s election in 1988 all the way through to 2024. Only Obama would have served as a break in between. Add in the Vice-Presidency and Secretary of State and there would have been a Bush or a Clinton within the presidential cabinet for 40 out of 44 consecutive years, from 1982 until 2024.
To put into context how unique that would have been in American history, the only other presidents from the same immediate family were John Adams and his son John Quincy Adams, and they served only a total of 8 years as president, with a 24-year gap separating Sr’s leaving office in 1801 from Jr’s being selected president (by Congress) in 1825. The two Roosevelts later racked up a total of 20 years as president – eight for Teddy and twelve for FDR – but they were only fifth cousins (though FDR’s wife Eleanor Roosevelt was Teddy’s niece), and they too were separated by a 24-year gap of non-Roosevelt governance, from 1909 to 1933. William Henry Harrison and his grandson Benjamin Harrison were president for 4 years (WHH died a month into his own presidency), 48 years apart.
The Bush and Clinton families by comparison really did have 20 uninterrupted years alternating as president, from 1988 to 2008. During this time they also had governorships in Texas (George W.), Florida (Jeb), and Arkansas (Bill), and a senatorship in New York (Hillary). (Bush Sr.’s father, Prescott Bush, had also been a senator, from 1952-1963, representing Connecticut). And then, of course, Jeb Bush and Hillary Clinton were thought to be the front-runners for the presidency a year before the 2016 elections.
It is difficult to know to what extent Americans’ wariness or resentment of the Bush and Clinton families helped the anti-establishment politicians who ran that year. In the Republican primaries in particular, about 45 percent of the votes went to Donald Trump. Another 25 percent went to Ted Cruz. In the Democratic primaries 43 percent of votes went to an independent candidate, Bernie Sanders. It is easy to imagine the Bush-Clinton dynamic played at least a small role in influencing the outcome of the 2016 elections.

I’ve had political dynasties on my mind in recent years not only because of American politics, but also because in my home country Canada, and home province Ontario, both of the politicians in charge, Justin Trudeau (since 2015) and Doug Ford (since 2018), have been in office mainly because of who their relatives were. Justin Trudeau is the son of the charismatic Pierre Elliot Trudeau, who was prime minister of Canada for 15 years between 1968 and 1984. Doug Ford is the older brother of Toronto’s infamous former mayor Rob Ford, who passed away in 2016, and the son of a provincial parliamentarian and businessman, Doug Ford Sr.
Both Trudeau and Ford were elected by their parties in times of political desperation. The Liberals picked Trudeau to become party leader following an election loss in 2011, in which the party had fallen to third place in a Canadian election for the first time in its history. He is the first child of a prime minister in Canada to ever become prime minister himself. The Ontario Progressive Conservatives meanwhile chose Doug Ford after being 15 years out of power, and after their previous party leader had been forced out in response to allegations of sexual misconduct several months before the 2018 provincial election was scheduled to take place.
In Mexico, political dynasts held the country’s presidency from 2006 until 2018, at which point the country’s current populist president, Andreas Manuel Lopez Obrador, was elected. From 2013 to 2018 Mexico’s president was Enrique Pena Nieto, both of whose uncles were former governors of the State of Mexico, the state in which Mexico City is located. From 2006 to 2012 the president was Felipe Calderon, whose father founded the political party that the younger Calderon went on to lead, the National Action Party. (In 2000, when Vincente Fox became president, the National Action Party ended a 71-year streak by the autocratic Institutional Revolutionary Party, which had governed since 1929). To become president in 2006, Calderon narrowly beat Andreas Manuel Lopez Obrador in one of the closest and most controversial elections in Mexican history. Obrador, who does not come from a political or upper class family, became a national figure as Mexico City’s mayor from 2000-2005.
Northeast Asia

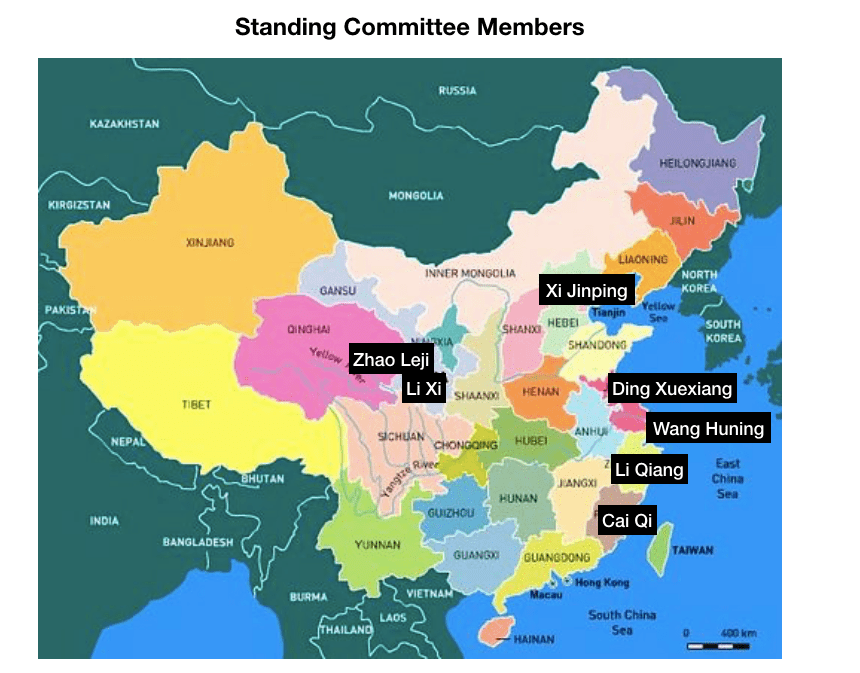
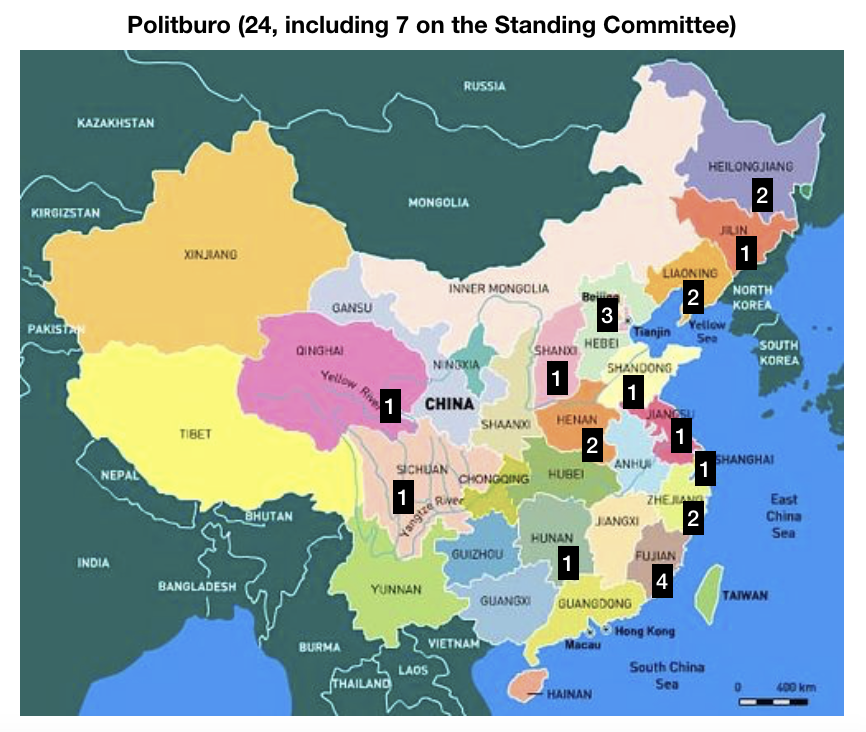
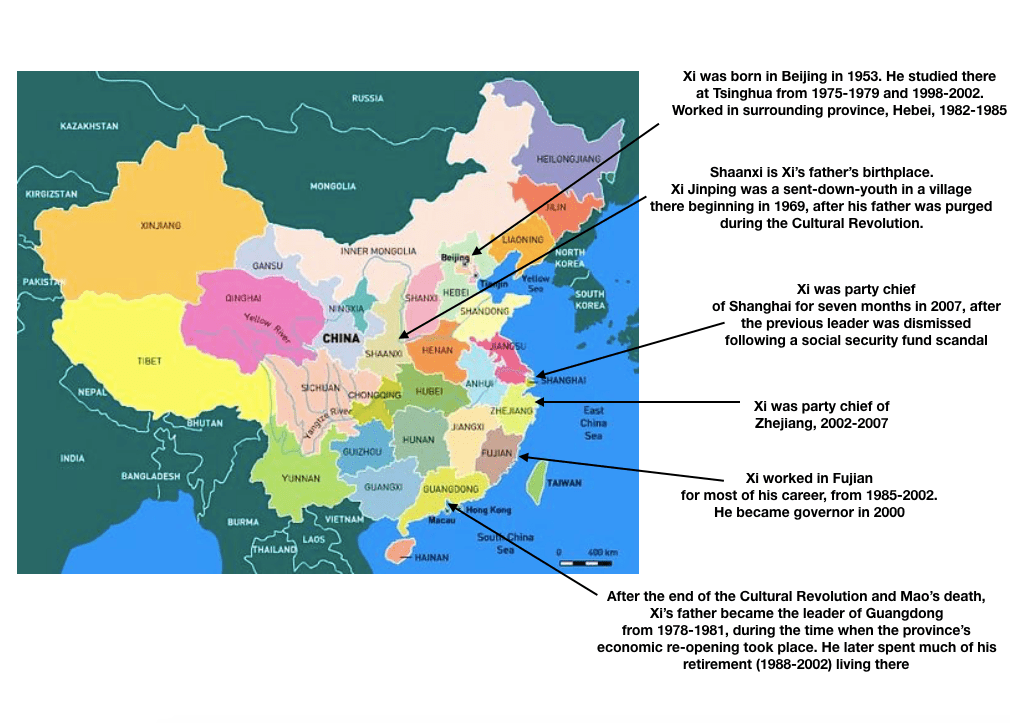
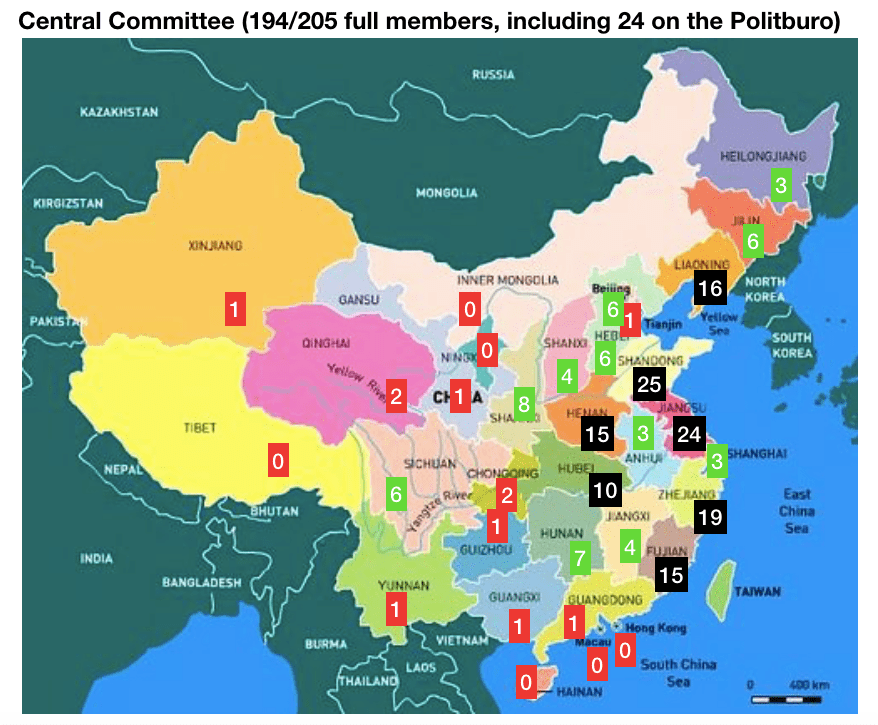
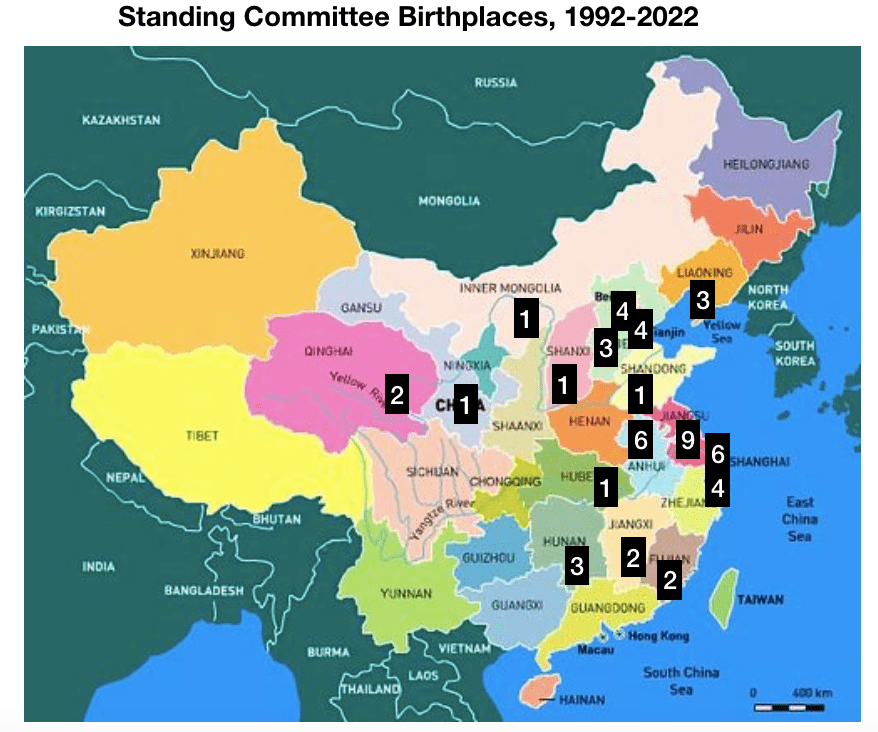
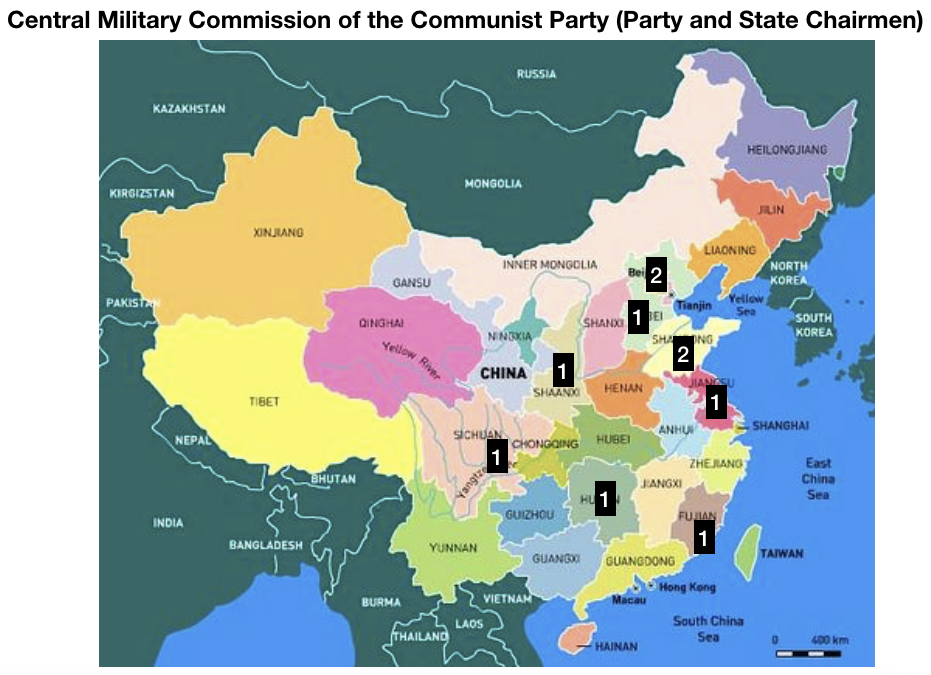
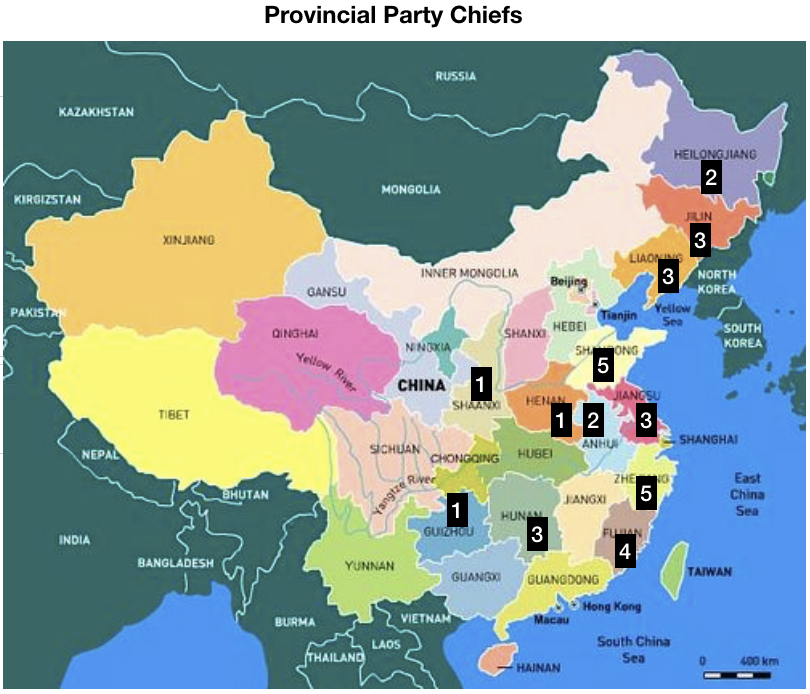
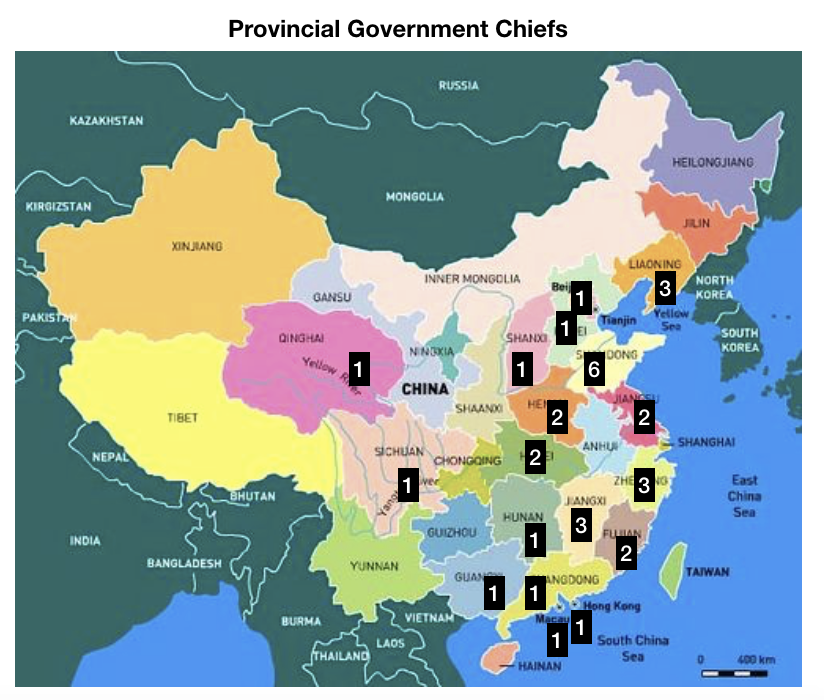
In China, the current General Secretary of the Communist Party, Xi Jinping, is the first to come from the “princeling” class. He is the son of a high-ranking political figure, Xi Zhongxun, who was part of the first generation of the Communist Party leadership. After being jailed for years during the Cultural Revolution, Xi’s father went on to preside over China’s Guangdong province when it led the way in China’s economic re-opening. Other prominent princelings include China’s current vice president Wang Qishan (though only by marriage), who arguably was China’s second most influential politician during the past decade, and Bo Xilai, who famously fell from power around the time Xi was promoted to General Secretary in 2012.
In Japan, former prime minister Shinzo Abe also came from a top political dynasty. His father was Foreign Minister during the 1980s, his paternal grandfather was an anti-militarist politician who died of a heart attack just before Japan’s post-WWII elections in 1946, and his maternal grandfather was one of Japan’s infamous 20th century leaders, Nobusuke Kishi. Kishi was a member of cabinet during WWII, was one of the major managers of Japan’s industrial puppet-state slave economy in Manchuria in the 1930s, and became prime minister of Japan from 1957-1960.
Like Xi Jinping, Shinzo Abe was probably the most important politician his country has had in recent decades. He retired from being prime minister in 2020 due to health reasons, and was assassinated earlier this year. The current prime minister, Fumio Kishida (who faced an assassination attempt earlier this week), is the son and grandson of former members of Japan’s House of Representatives.
Many of Japan’s lawmakers are from political families. Taro Aso, for example, who was Japan’s prime minister from 2008-2009 and deputy prime minister from 2012-2021, is the grandson of a former prime minister, the son-in-law of another prime minister, and a relative of Japan’s emperor Akihito by marriage. Aso is now the vice president of Japan’s ruling Liberal Democratic Party (ranking just behind prime minister Kishida), even though he previously led the party to its worst electoral defeat – one of only two losses since WWII – in 2008.
Akihito, meanwhile, traces his own imperial family’s roots back at least 1483 years. He was emperor for 30 years before abdicating in favour of his son in 2019. His father, Hirohito, reigned for 63 years, the longest of any of the nearly 100 historically verifiable Japanese emperors.
The president of South Korea, Moon Jae-in, was born to North Korean refugees and grew up in poverty. The previous president however was Park Geun-hye, the daughter of South Korea’s longest-serving president, Park Chung-hee. The elder Park came to power in a military coup in 1961, and served as president from 1963 until he was assassinated in 1979. (His wife – Park Geun-hye’s mother – was also assassinated, in 1974, a casualty of an earlier failed attempt on her husband’s life). Park Geun-hye was South Korea’s first female president from 2013 to 2017, but was then impeached on corruption charges, and spent several years in prison.
In North Korea, the Kim family’s rule is now roughly 74 years old, and 12 years into its third generation. But the Kim regime will have to survive for another quarter century, all the way to 2058, if its current leader Jong Un is to surpass his grandfather Kim Il Sung’s 46-year reign (from 1948-1994).
South Asia

In India in 2014, Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party became the first party in over three decades to win a majority government in a national election. Modi is not from a political dynasty himself, rather he is (among other things) a reaction against the modern world’s most prominent political family of all: the Nehru-Gandhi dynasty.
The Nehru-Gandhi dynasty – which is not related to the Gandhi – began with Jawaharlal Nehru, India’s first post-British prime minister from 1947 until 1964. Nehru was himself the son and nephew of political figures in pre-independence India. Nehru’s dynasty continued with his daughter Indira Gandhi (née Nehru), who was India’s prime minister from 1966-1977 and 1980-1984. Indira was assassinated in 1984, two months before a general election; her son Rajiv Gandhi took over and received a record number of votes in that conflict-ridden election, but was then voted out of office in 1989. Rajiv ran again in 1991, but was assassinated a month before the election. His wife, Sonia Gandhi, has presided over India’s Congress Party ever since then. (The Congress Party held the office of prime minister in 55 out of India’s 67 years of independence prior to Modi’s being elected). Their son Rahul Gandhi was Modi’s main opponent in both of Modi’s electoral wins, in 2014 and 2019.
In Pakistan, current prime minister Shehbaz Sharif is the brother of Nawaz Sharif, who previously served as prime minister from 1990-1993, 1997-1999, and more recently 2013-2017. Shehbaz Sharif took over from the previous prime minister, former cricket star Imran Khan, as part of a constitutional crisis earlier this year. The third Sharif brother, Abbas, was also a member of parliament in the 1990s. Nawaz’ daughter Maryam has recently entered politics as well, becoming a high-ranking member of their current governing party (which her father founded in 1993), the Pakistan Muslim League.
Pakistan’s new foreign minister, Bilawal Bhutto Zardar, is the son of two former leaders: former prime minister Benazir Bhutto and former president Asif Ali Zardari. (Benazir Bhutto was assassinated in 2007 soon after her return to the country following eight years in exile, two months after an earlier failed assassination attempt at her return parade killed an estimated 180 bystanders). He is also the grandson of Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, Benazir’s father, who had served as prime minister and as president of Pakistan before being executed in 1979 following a coup.
In Bangladesh, Sheikh Hasina has been prime minister for 18 years, from 1996-2001 and again since 2009. Her father Sheikh Mujibur Rahman was the founding president of Bangladesh after it became independent of Pakistan in 1971, and served as prime minister from 1972 until 1975, when he, his wife, and his three sons were assassinated during a military coup. After the coup Ziaur Rahman (unrelated to Mujibar) rose to power, but was assassinated in another coup in 1981. (In between these two coups there was another, unusual coup attempt, which was sparked when Japanese Red Army airplane hijackers landed a flight from India in Bangladesh in 1977. More than 1100 military personnel were hanged in two months following the coup’s failure). Before he was overthrown in 1981, Ziaur allowed Sheik Hasina to return to the country.
Ziaur’s widow Khaleda Zia became prime minister in the early 1990s and again in the early 2000s, and remains the leader of the Bangladesh Nationalist Party. Uniquely, Bangladesh’s politics have therefore been dominated by two women in the past generation. Meanwhile in West Bengal – India’s populous Bengali state, just across the border from Bangladesh – the chief minister since 2011 has been a self-made woman, Mamata Banerjee. She is currently the only woman among the 30 chief ministers of India’s states.
Southeast Asia

The Philippines may be the best example of a democracy dominated by political dynasties. Earlier this year, Ferdinand “Bongbong” Marcos was elected president, along with Sara Duterte-Carpio as his vice president. Bongbong’s father Ferdinand Marcos Sr. was president for 21 years, from 1965-1986, mostly ruling as a dictator with the country under martial law. Bongbong’s mother, famous First Lady Imelda Marcos, was governor of Manila for 11 years, a member of parliament for 18 years (most recently from 2010-2019), and twice ran for president in the 1990s. Bongbong’s wife, son, daughter, and nephew also ran for various political offices in 2022. His vice president, Sara Duterte-Carpio, is the child of a notorious political leader too: Rodrigo Duterte, who was president until his term ended earlier this year. Sara Duterte’s grandfather and great uncle were also fairly prominent politicians.
In the election that brought Rodrigo Duterte to power in 2016, roughly two-thirds of the Philippines’ outgoing Congress had been heirs of political families. Before Duterte, the country’s president was Benigno Aquino III, whose mother Corazon Aquino (president from 1986-1992) had led the uprising against the dictator Ferdinand Marcos after her husband Ninoy Aquino, a senator and leading political opponent of the Marcos regime, had been assassinated in 1983. Before Benigno Aquino, the president was Gloria Macapagal Arroyo (2001-2010), the daughter of Diosdado Macapagal (president from 1961-1965).
In other words, three of the four presidents since 2001 have been children of earlier presidents, and the only exception, Rodrigo Duterte, is the father of the new vice president.
[2024 Update, from Semafor: “Filipino politics has taken a turn for the macabre, as the vice president threatened to exhume the corpse of the president’s father, and admitted to imagining ‘chopping off‘ the president’s head. Relations between the families of President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. and Vice President Sara Duterte-Carpio hit an all-time low with the remarks, against the backdrop of the two dynasties’ ongoing feud. Duterte-Carpio said she would throw the body of the president’s father, the dictator Ferdinand Marcos Sr., into the sea. The vice president also luridly described thoughts of murdering the president that were spurred by refusing a request to give his watch as a graduation gift.”]
In Indonesia, the president since 2014, Joko Widodo (Jokowi), was the first of his generation not to have come from an established political or religious family or from the military. Megawati Sukarnoputri, by contrast, who was previously Indonesia’s president from 2001-2004 and now serves in Jokowi’s cabinet, is the daughter of Sukarno, Indonesia’s first post-independence president from 1945-1967. And Jokowi’s son Gibran was elected mayor of Surakarta, a major city in central Java, in 2021, where Jokowi had previously been mayor from 2005-2012.
Update: Jokowi’s son Gibran became Indonesia’s vice-president in February 2024, at the age of 36, running with former general Prabowo Subianto, the newly elected president.
Prabowo’s ex-wife was the daughter of Indonesia’s former military dictator Suharto, who ruled from the fall of Sukarno in 1967 until the East Asia financial crisis in 1998. 1998 was also the year of Prabowo’s divorce from Titiek Suharto, and his dishonourable discharge from the military, on the accusation of having incited anti-Chinese pogroms during that year’s riots. (Suharto’s son, Tommy, ran for president in 2019 – as did Prabawo, who was defence minister at the time – despite having been accused of carrying out several bombings and the attempted assassination of a judge when members his family began being prosecuted in 1999. Tommy Suharto’s party received only about 2% of the vote in 2019).
In addition to Jokowi’s son becoming Probowi’s VP this year, Jokowi’s son-in-law Bobby Nasution has been the mayor of Medan, the largest city on Sumatra, since 2021. According to the East Asia Forum, “Dynastic politics in modern democratic Indonesia is well and truly entrenched, forming the bedrock of several leading political parties…Former president Megawati Sukarnoputri, the daughter of Indonesia’s founding president Sukarno, is the matriarch of a dynasty now three generations old which controls Indonesia’s largest political party, the Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle….Jokowi’s youngest child Kaesang Pangarep, an entrepreneur, YouTuber and soccer club owner, indicated that he is also preparing to enter politics.”
In Malaysia, the leading political figure has been Mahathir bin Muhammad, prime minister from 1981-2003 and again from 2018-2020. He was the first one of Malaysia’s prime ministers not born into a well-known political, business, or religious family. Before Muhammad’s return to power (at 93 years old), the prime minister from 2009-2018 was Najib Razak, who was the son of Malaysia’s second prime minister Abdul Razak Hussein and the nephew of Malaysia’s third prime minister Hussein Onn. (Malaysia’s first prime minister, from 1957-1970, was the seventh son of a sultan). The current prime minister Anwar Ibrahim, like Mahathir bin Muhammad, does not come from an influential family. He had been one of Muhammad’s deputy prime ministers in the 1990s, but was then was imprisoned on charges of sodomy until Muhammad left office in 2004. He received a royal pardon in 2018.
In Singapore, the prime minister since 2004 has been Lee Hsien Loong, the son of modern Singapore’s founding leader, Lee Kuan Yew. Lee Kuan Yew was prime minister of Singapore from 1959-1990, a cabinet minister until 2011, and a member of parliament for 60 years, from 1955-2015.
In Myanmar, Aung San Suu Kyi became prime minister in 2016. She had spent 15 years under house arrest in the aftermath of an election victory in 1990, the election result having been annulled by the military. She was elected again in 2020, but was then overthrown by another military coup and sentenced to 20 years in prison. Her father, Aung San, was modern Burma’s founding leader, who was assassinated along with most of his cabinet just before the country became independent in 1948. Her uncle, Thaksin Than Tun, later led the Communist Party of Burma, and was assassinated in 1968.
In Vietnam, the leading General Secretary of the Communist Party since 2011, Nguyễn Phú Trọng, lists “average peasant” as his background in his official biography. The previous General Secretary, Nông Đức Mạnh (2001-2011), was however rumoured to have been the illegitimate son of Hồ Chí Minh. (According to Wikipedia, “In April 2001, shortly after Nông Đức Mạnh was named as General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam , a reporter at a news conference asked him to confirm or deny the rumor. He responded, “All Vietnamese people are the children of Uncle Hồ.)” In 2016, “the sons of Prime Minister Nguyen Tan Dung were newly elected… The older son, Nguyen Thanh Nghi, is one of the youngest provincial party chiefs in Vietnam. He is 39 years old. The younger son, Nguyen Minh Triet, 25, was also selected to be a member of the party committee of Binh Dinh province”.
In Cambodia, King Norodom Sihamoni has reigned since 2004. His father, the filmmaking king Norodom Sihanouk, reigned from 1941-1955 and 1993-2004. Sihanouk’s first kingship began at 19 years old, during WWII when Cambodia was governed by a mix of Vichy France, imperial Japan, and Japan’s regional ally Thailand. Uniquely, he abdicated the throne in favour of both his own father (in 1955) and son (in 2004). His 1955 abdication was carried out so that he could participate directly in Cambodian politics. His father took over his role as king until dying in 1960, and his mother reigned as queen from 1960 to 1970, when a coup swept both her and her son from power. She died in exile in Beijing in 1975, only ten days after the Khmer Rouge conquered the Cambodian capital Phnom Penh.
Sihanouk came back from his own exile in China and North Korea in 1975, to serve briefly as a figurehead president during the Khmer Rouge regime. After the Khmer Rouge were ousted by Vietnamese forces in 1979, he went into exile again in 1981. He became king for the second time in 1993, following elections that brought to power a coalition government composed of his son Norodom Ranaridd (a half-brother of Cambodia’s current king) and Hun Sen, Cambodia’s dominant politician.
Hun Sen has led Cambodia since 1984. He has held the post of prime minister for nearly three decades, and is now 71 years old. In 2018 Hun appointed one of his sons, Hun Manet, to high-ranking military and political positions. Manet was promoted again several months ago. It is now thought that he might succeed his father as Cambodian prime minister as soon as this summer.
The nearby Sultan of Brunei, Hassanal Bolkiah, has similarly been prime minister since 1984. But he has also been the sultan since 1967, making him (since Queen Elizabeth’s passing) the longest-lasting state leader in the world today.
Finally, in Thailand, there are two dynasties of note: the monarchy and the Shinawatras. The monarchy, which is one of the wealthiest in the world, is currently helmed by King Vajiralongkorn, who had previously spent 50 years as the crown prince. His father, Bhumibol Adulyadej (Rama IX), was king from 1946-2016, a 70-year reign that is tied with Queen Elizabeth’s for history’s longest as an adult sovereign. He was widely revered and respected, whereas the new king Vajiralongkorn is for many reasons a problematical figure (far more so than, for example, King Charles). But it is difficult for people in Thailand to criticize him, as the royal family is covered by extremely strict lèse-majesté laws.

The Thai military, often allied with the monarchy, has played a leading role in the country’s politics. The prime minister from 2001-2006, Thaksin Shinawatra – the son of a former member of parliament and a minor member of the royal family of the old kingdom of Chiang Mai – was overthrown by a military coup, following a political crisis in which Shinawatra was alleged to be an anti-monarchical leader. His younger sister Yingluck Shinawatra later became prime minister from 2011-2014, before being removed during the Thai political crisis in 2013-2014, which ended in another coup, endorsed by the former king. The military-monarchy alliance has remained in power since.
During elections in 2019, King Vajiralongkorn’s elder sister, Princess Ubol Ratana, tried to become prime minister as the candidate of a political party supported by the exiled Shinawatras. The king immediately denounced the move as unconstitutional and the party was banned from politics for a decade.
Now, however, Thaksin Shinawatra’s 36-year-old daughter Paetongtarn Shinawatra (Yingluck’s niece) appears likely to become Thailand’s next prime minister. Elections will be held on May 14th.
—
Additional Notes for Part 1:
- The Ford family’s list of scandals is long, in addition to the crack-smoking video which made Rob famous while mayor of Toronto. Doug and his brother Randy were medium-sized drug dealers when they were younger, and in the 1990s were accused of kidnapping a fellow drug dealer who owed them $5000 dollars. (This did not stop their father and Rob from attempting to carve out war-on-drug reputations in municipal politics. Rob’s attempt to do so was derailed by an early arrest for impaired driving in Florida, one of the family’s numerous DUIs). The Fords’ ex-brother-in-law meanwhile was convicted of murdering their sister’s new lover, a white supremacist, in 1998. That same sister (who is the mother of Ontario’s new minister of citizenship and multiculturalism, Michael Douglas Ford, elected in 2022) had another boyfriend taken into custody for allegedly trying to kill Rob Ford in 2012, and was shot in the face, maybe accidentally, by that boyfriend and another man in 2005.
- The saddest and strangest dynastic episode in recent history took place in Nepal, in 2001. There, in the middle of civil war (1996-2006), the heir to the throne, crown prince Dipendra, is alleged to have carried out a mass shooting inside the royal palace, killing his father the king, his mother the queen, seven other siblings or cousins, and then shooting himself as well. He survived the suicide attempt for three days, in a coma, and despite his murders he was officially declared the new king, while comatose. After his death the kingship passed to his uncle, Gyanendra. There are many conspiracy theories about this royal massacre, including suggestions that it was really Gyanendra who was behind the attack, since it resulted in his becoming king and since his own immediate family members, who had been present during the attack, were said to have been relatively unscathed. Gyanendra had actually been king previously as well, from 1950-1951 when he was three or four years old, during a period when most of the rest of the royal family fled to India. His second kingship lasted only from 2001-2008, when Nepal abolished its monarchy altogether. But he is still involved in Nepalese politics today.
- In Cuba, Fidel’s death in 2016 and Raul’s retirement and death in 2021 have left the island without a Castro in charge for the first time in 62 years.
- The most successful American dynasty of all, the Kennedy family, recently lost its long hold on high office. Ted Kennedy’s death in 2009 ended his nearly 47-year tenure in the Senate, the fourth-longest such tenure in American history, which he had begun when he took over his brother JFK’s seat in Massachusetts at the start of the Kennedy presidency in 1962. Then in 2011 Ted’s son Patrick Kennedy retired from Congress, ending a streak of 68 consecutive years with a Kennedy in high office, going all the way back to 1947 when JFK was elected to Congress. By 2013, however, RFK’s grandson (and son of former Congressman Joseph Patrick Kennedy II) Joe Kennedy III was elected to the House, where he remained until losing a Democratic primary in an attempt to become a senator in 2020. That made him the first Kennedy to ever lose an election in Massachusetts, leaving Congress without a Kennedy again. But his uncle RFK Jr. just announced he is running against Biden to become the Democratic nominee for president in 2024.
- Multiple members of the Bush family were involved, directly or indirectly, in the events in Florida that decided the 2000 presidential election. Jeb was Florida’s governor at the time. George H W Bush had appointed Clarence Thomas and David Souter to the Supreme Court, which then in effect narrowly ruled (5 to 4, though admittedly Souter was among the 4) to stop the statewide election recount that the Florida Supreme Court had ordered. Even George and Jeb’s first cousin, John Ellis, was involved in the election over at Fox News, as head of its election night decision desk. Fox was the first news network to call Florida for Bush on the night of the election, leading the other major networks to temporarily follow suit, before all of them, including Fox, retracted their calls. Cousin John’s role is perhaps somewhat reminiscent of a more recent electoral event: the Dominion lawsuit payout, a story which similarly began with Fox News being the first to call the 2020 election (via Arizona) for Biden. And of course, John was not the last Bush cousin to be involved in the late stages of an election. The cousin Billy Bush-Donald Trump Access Hollywood tape was aired one month before the 2016 election.
- Gore too came from a political family: he and his father served in the House of Representatives, Senate, or as vice president for all but six years from 1939-2001
- Hillary Clinton meanwhile was also elected in 2000, as a senator representing New York, immediately following the end of her husband’s presidential term. She beat Republican Rick Lazio after the presumptive nominee, mayor Rudy Giuliani, was diagnosed with cancer and faced a series of setbacks and scandals earlier in the year. During this same time, Giuliani also inserted himself into the Elian Gonzales affair, repeatedly calling the US agents who forcibly retrieved Gonzales “storm troopers”. The Gonzales affair, in turn, might also have helped swing the 2000 presidential election. (Gonzales, by the way, was elected to Cuba’s parliament this past week, at the age of 29. By coincidence, this occurred the day before the Dominion lawsuit was settled, a week after a new Giuliani audio tape, recorded secretly by a Fox employee, emerged in that suit).
- Pierce Bush, a nephew of Jeb and George W., ran unsuccessfully for Congress in 2020
- Theodore Roosevelt and Franklin D. Roosevelt came somewhat close to facing one another in the 1920 presidential election. Teddy had already been president previously, and had afterward founded his own Progressive party, becoming in the 1912 election “the only third party presidential nominee to finish with a higher share of the popular vote than a major party’s presidential nominee. [He got more votes than William Howard Taft, who had been the incumbent president and yet finished a distant third behind Woodrow Wilson and Roosevelt]”. But Teddy became the Republican front-runner again ahead of the 1920 election, after rejoining the party. He died however in 1919, and Warren Harding became the Republican nominee and president instead. (Harding then appointed Taft, an ex-president, to the Supreme Court – a unique situation) . Meanwhile FDR, then only 38 years old, was the Democratic vice-presidential nominee in the 1920 election, facing Harding’s running mate Calvin Coolidge. Both Coolidge and FDR later became presidents themselves.
- The Adams family came fairly close to spending three generations at the top of American politics. John Adams was the country’s second president, taking over from George Washington in 1797. His son John Quincy Adams won the 1825 election without receiving a majority of the electoral college seats – he only got 38% – but was chosen to become president by the House, the only president this ever happened to. 24 years later, John Quincy’s son ran for vice-president as part of Martin Van Buren’s Free Soil Party ticket in 1848, but lost.
- According to Wikipedia, Abe’s grandfather Nobusuke Kishi was referred to as the “Monster of the Shōwa era“…. “when he was locked up in Sugamo prison in 1946 [a decade before becoming Prime Minister], awaiting trial, he reminisced about his Manchukuo [Japanese-ruled Manchuria] years: “I came so much, it was hard to clean it all up”.
- In the Dominican Republic, the president since 2000 has been Luis Abinader, whose father José Rafael Abinader Wasaf was a senator and wealthy businessman, who founded the political party that the younger Abinader now leads.
- In Sri Lanka, mass protests this summer forced the resignation of president Nandasena Gotabaya Rajapaksa, a week after protestors broke into and partied in the presidential mansion. In addition to being president, Rajapaksa is the brother of the former prime minister Mahinda Rajapaksa, who previously also served as president from 2005-2015. Their other brother, Chamal, was speaker of the parliament. The Rajapaksas have long been a political dynasty, with many past and present members in Sri Lankan politics. The country’s new president similarly comes from a major political family.
- Sanjay Gandhi, Indira’s elder son, died while piloting an airplane in 1980, not long before Indira’s assassination in 1984 and Rajiv’s in 1991. (This is one reason the Gandhis are often compared with the Kennedies). He had been made secretary general of the Congress Party only a month before his death, not long after playing a controversial role during the Emergency. For example (according to Wikipedia) “In September 1976, Sanjay Gandhi initiated a widespread compulsory sterilization program to limit population growth. The exact extent of Sanjay Gandhi’s role in the implementation of the program is disputed, with some writers holding Gandhi directly responsible for his authoritarianism, and other writers blaming the officials who implemented the programme rather than Gandhi himself”. Sanjay too survived an assassination attempt during the following election campaign, his first, in 1977. (A year later, two men hijacked a passenger airplane for several hours and demanded that Indira be released from prison – she was arrested after the Emergency – and various charges against Sanjay be dropped. The two hijackers were rewarded by the Congress party for doing this, by being made parliamentary candidates in Uttar Pradesh in 1980. Both won and served multiple terms).
- Sanjay’s wife, Maneka Gandhi, has however since jumped ship from the Gandhi-dominated Congress Party and joined the rival BJP. She is currently a cabinet minister in the BJP-led government. Maneka’s son Varun has also gone over to the BJP, serving as the youngest National Secretary in the history of the party and a member of the country’s parliament. But Maneka and Varun both remain less prominent than the Congress side of the family, which is led by Maneka’s sister-in-law Sonia and Varun’s first cousins Rahul and Priyanka Gandhi.
- The BJP is arguably just as dynastic as the Congress party is, or at least not so far off. According to the Economist “nearly a third of lawmakers in India’s lower house come from political families”. Family politics are also extremely common within India’s diverse, influential state governments. In Tamil Nadu for example the chief minister, M.K. Stalin (born four days after Joseph Stalin’s death in 1953) is the son of Tamil Nadu’s longtime Chief Minister Muthuvel Karunanidhi. In India’s most populous state, Uttar Pradesh, the Yadavs’ Socialist Party has been influential, while in the second most populous state, Maharashtra, the Thackeries’ Army of Shiva Party has been even more influential. The longest incumbent among current chief ministers, Odisha’s Naveen Patnaik (in power since 2000) is the son of a previous chief minister too. These are just a few examples of prevalent dynasticism in India.
- In Bhutan, the current dragon king is the fifth in a dynasty that has reigned since 1907. He became king in 2006, when his father (still living today) abdicated the throne at the age of 54. His father had become king in 1972, at the age of 17. In 1975, Bhutan’s fellow Himalayan kingdom, Sikkim (it is wedged right between Bhutan and Nepal) joined India; Bhutan is now the last of these kingdoms, since Nepal abolished its own monarchy in 2008.
- The royal family of Sikkim comes originally from Tibet. Tibet, of course, has its own hereditary leadership, of a sort, with figures like the Dalai Lama and the Panchen Lama. The current 14th Dalai Lama was given political power following the battle of Chamdo in 1950, at the age of 15, a decade after his enthronement as a child. According to Wikipedia: “The current 11th Panchen Lama, Gedhun Choekyi Nyima, was recognized by the 14th Dalai Lama on 14 May 1995. Three days later, the six-year-old Panchen Lama was kidnapped by the Chinese government and his family was taken into custody. The Chinese government instead named Gyaincain Norbu as the 11th Panchen Lama. Their nomination has been widely rejected by Buddhists in Tibet and abroad, while governments have called for information about and the release of the Panchen Lama. Gedhun Choekyi Nyima has never been publicly seen since 1995″.
- India too had royal-run regions – the princely states – until its post-independence period. “At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent…In 1947, princely states covered 40% of the area of pre-independence India and constituted 23% of its population”. Hyderabad, by far the most significant of these princely states, was home to about 16 million people, with a territory nearly the size of Britain, when its princely status was ended in 1948 after it was briefly invaded by India. (The last Nizam of Hyderabad had 34 children; his second son married a daughter of the last Ottoman crown prince and caliph in 1930, several years after the Ottoman sultanate and caliphate ended). The other large princely state was Jammu and Kashmir, which was religiously the opposite of Hyderabad: its rulers were Hindu but its population was mostly Muslim, whereas Hyderabad’s rulers were Muslim but its population was mostly Hindu.
- Many of the heirs of the numerous princely states are still rich or influential today, to varying extents. Perhaps the most intriguing one is Balthazar Napoleon IV de Bourbon, who lives in Bhopal. “It is claimed that this family is legitimate descendant of the House of Bourbon, descended from Jean Philippe de Bourbon, an exiled French noble who served in Mughal Emperor Akbar’s court. In his book, Prince Michael of Greece and Denmark says that he believes Jean de Bourbon was a nephew of the first Bourbon French king, Henry IV. While this hasn’t been proved fully yet, it is notable to mention that if true, Balthazar Bourbon would be first in line for the French throne.”
- In Pakistan, according to Wikipedia, “The son of a wealthy industrialist, Mr Sharif worked in the family business before entering politics. While his brother had three terms as prime minister, Shehbaz, now 70, had three terms as chief minister of the country’s most populous province, Punjab. His first stint was cut short by a military coup in 1999, when the army ousted the elder Sharif as prime minister and both brothers temporarily went into exile. Like Nawaz, he has also been accused of corruption.”
- In Taiwan, Chiang Kai-shek’s son Chiang Ching-kuo was president from 1978-1988, and Chiang Hsiao-yen – thought to be an illegitimate son of Chiang Ching-kuo – was Vice Chairman of their Nationalist party (Kuomintang) from 2009–2014. Chiang Kai-shek’s adopted son Chiang Wei-kuo was also a significant political and military figure. (Chiang Kai-shek was China’s Nationalist leader from 1928-1975, ruling as autocrat in Taiwan after fleeing the mainland at the end of the Chinese Civil War. His son Chiang-kuo “was sent as a teenager to study in the Soviet Union during the First United Front in 1925, when his father’s Nationalist Party and the Chinese Communist Party were in alliance…but when the Chinese Nationalists violently broke with the Communists, Stalin sent him to work in a steel factory in the Ural Mountains. [He was kept there as a political prisoner and potential bargaining chip]. There, Chiang met and married Faina Vakhreva. With war between China and Japan imminent in 1937, Stalin sent the couple to China.” Ching-kuo later governed Taiwan for a decade until his own death, but also ended its long era of martial law in 1987.
- Taiwan is also home to an heir (at least symbolically) of Confucius, a 79th-generation descendant who has had an advisory role in politics. The supposed or ceremonial heirs of the other of the Four Sages have also had roles of this kind. Meanwhile in the mainland, a descendant of the Qing dynasty played a small part in Beijing politics, before retiring in 2008. So too have the heirs of the Ming, the preceding dynasty which lost the emperorship around 1644. China’s premier from 1998-2003, Zhu Rongji, may have been descended from the first Ming emperor who ruled in the 14th century. [When the Ming’s successors, the Qing, were overthrown just before WWI, the idea of either the 76th-generation Duke Yansheng (thought to be a descendant of Confucius) or the heir of the dormant Ming dynasty becoming China’s new emperor was considered. But neither happened. Instead, general Yuan Shikai declared himself emperor in 1915 – a move that lasted only four months. Later, the final Qing emperor Puyi became emperor of Japanese-controlled Manchuria from 1934 until the end of WWII. Puyi had previously been China’s emperor when he was a child. In 1966, during the Cultural Revolution, “The Cemetery of Confucius was attacked by a team of Red Guards from Beijing Normal University….The corpse of the 76th-generation Duke Yansheng was removed from its grave and hung naked from a tree in front of the palace during the desecration of the cemetery.” That same year Red Guards also damaged the tomb of the Wanli emperor, who had the longest reign of any Ming emperor]. More recently, Mao’s grandson became the youngest general in China’s military, in 2009. But he is not a significant figure.
- Kim Jong Il’s eldest son Kim Jong-nam, who was Kim Jong Un’s half-brother, was assassinated in 2017 at the airport in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Kim Jong Il’s sister’s husband, Jang Song-thaek, was executed by firing squad in 2013.
Part 2 – The Middle East